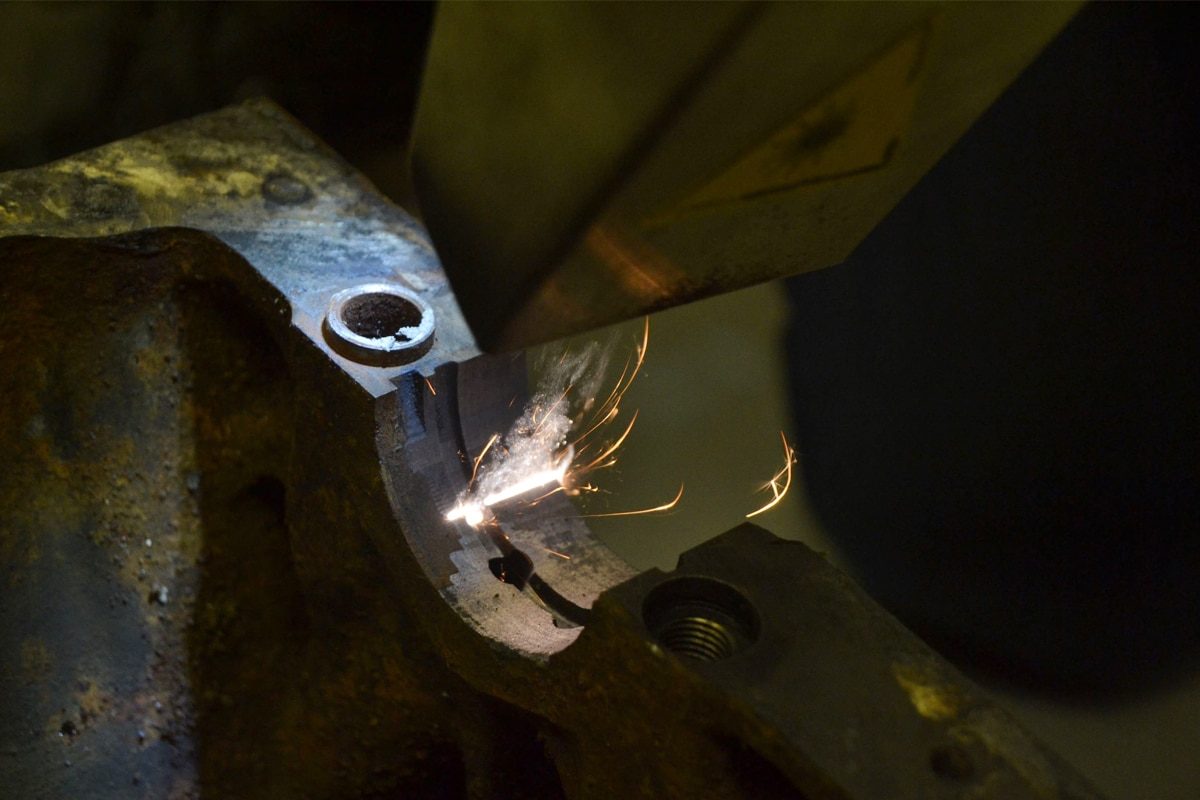


Understanding Rust and Its Impact
The Nature of Rust
The Chemistry of Rust Formation
Rust forms through an electrochemical process involving the following steps:
- Anodic Reaction: Iron atoms lose electrons and form iron ions.
- Cathodic Reaction: Oxygen and water molecules combine with the electrons to form hydroxide ions.
- Formation of Rust: Iron ions and hydroxide ions interact to form hydrated iron oxide (rust).
Types of Rust
- Surface Rust: Affects the outermost layer; easier to remove.
- Pitting Rust: Creates holes and depressions in the metal, requiring more invasive treatments.
- Scale Rust: Thick, layered rust that forms under harsh environmental conditions.
Economic and Structural Impact
Economic Costs
Rust and corrosion represent a significant economic burden globally, costing an estimated $2.5 trillion annually, equivalent to over 3% of the world’s GDP. These costs stem from:
- Direct Expenses: Repairing or replacing rusted components, increased maintenance, and purchasing anti-corrosion materials.
- Indirect Losses: Production downtime, loss of product quality, and reduced operational efficiency.
Structural Integrity
Rust compromises the strength and stability of metal structures and components. Key effects include:
- Weakened Load-Bearing Capacity: Rust eats away at the metal, reducing its ability to support weight and withstand stress. This is critical in industries such as construction and transportation.
- Increased Failure Risk: Machinery, vehicles, and structural components are prone to breakdowns, accidents, or catastrophic failures when affected by rust.
- Safety Hazards: Rust-induced failures pose risks to personnel and the surrounding environment, making rust prevention and removal a top priority in sectors like aerospace, marine, and infrastructure.
Environmental Impact
Neglecting rust can lead to additional environmental damage, such as:
- Contaminated Soil and Water: Corroded materials leaching into the environment.
- Waste Generation: Increased waste due to discarded rusted components.
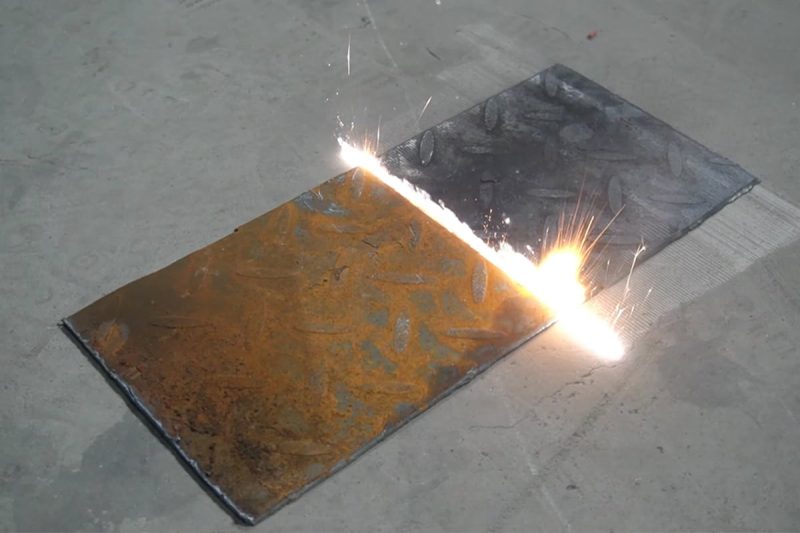

Laser Rust Removal
What is Laser Rust Removal?
How Does It Work?
Laser rust removal relies on the interaction between laser energy and the material’s surface to vaporize or dislodge rust. Here’s how it works:
- Energy Absorption: The laser beam is directed onto the rusted surface. Rust absorbs the laser’s energy more effectively than the underlying metal due to differences in reflectivity and thermal properties.
- Thermal Expansion: The intense heat causes the rust layer to expand rapidly, creating stress that separates it from the base material.
- Vaporization and Ablation: As the laser energy intensifies, the rust layer vaporizes or is ablated into fine particles, leaving a clean surface behind.
- Minimal Heat Transfer: Short, pulsed laser bursts minimize heat transfer to the surrounding material, preventing thermal damage to the substrate.
- Advanced laser cleaning systems allow precise control of parameters such as wavelength, power, and pulse duration, ensuring that only the rust layer is removed.
Advantages of Laser Rust Removal
- High Precision: Laser rust removal offers exceptional precision, enabling selective cleaning without harming the base material. This is particularly valuable for delicate or high-value components.
- Non-Contact and Non-Abrasive: The process does not involve mechanical force, ensuring there is no wear or surface damage, even on intricate designs.
- Environmentally Friendly: Laser cleaning is a green solution, generating minimal waste and eliminating the need for hazardous chemicals or abrasive media. The removed rust particles can often be captured with simple filtration systems.
- Low Maintenance: Laser cleaning systems have few consumables and require minimal maintenance compared to abrasive methods.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of materials, laser rust removal is effective on metals, composites, and more. It also works on various contaminants, such as coatings, oils, and dirt.
- Ease of Automation: Laser cleaning systems can be integrated into automated production lines, improving efficiency and consistency for large-scale operations.
- Long-Term Cost Savings: Although the initial investment is high, the long operational life and reduced consumable costs can make laser rust removal more economical over time.
Disadvantages of Laser Rust Removal
- High Initial Cost: Laser systems require a significant upfront investment, which may be a barrier for smaller businesses.
- Limited Speed on Large Areas: The focused nature of laser beams makes them less efficient for cleaning very large surfaces compared to abrasive methods like sandblasting.
- Energy Consumption: High-powered laser systems can consume substantial energy, impacting operational costs in energy-intensive settings.
- Safety Requirements: Proper safety measures are essential, including laser safety glasses and enclosures, to protect operators from potential hazards such as laser exposure.
- Skill and Training: Operators need specialized training to handle laser equipment and optimize settings for different applications.
Applications Beyond Rust Removal
Laser cleaning technology is highly versatile and is used for numerous applications beyond rust removal:
- Surface Preparation: Laser cleaning is ideal for preparing surfaces for welding, bonding, or coating, as it effectively removes contaminants without altering the surface profile.
- Paint and Coating Removal: It can strip paint or coatings from metal, wood, or composite materials without damaging the underlying structure.
- Oil and Grease Removal: Laser cleaning efficiently removes oils and greases, making them valuable in maintenance and repair operations.
- Mold Cleaning: Industries such as plastics and automotive manufacturing use lasers to clean molds without causing wear or deformation.
- Restoration and Conservation: Laser cleaning is widely employed in restoring historical artifacts, sculptures, and monuments, as it preserves the original material.
- Precision Cleaning in High-Tech Industries: Sectors like aerospace, electronics, and medical device manufacturing use laser cleaning for delicate components that demand high levels of cleanliness and precision.
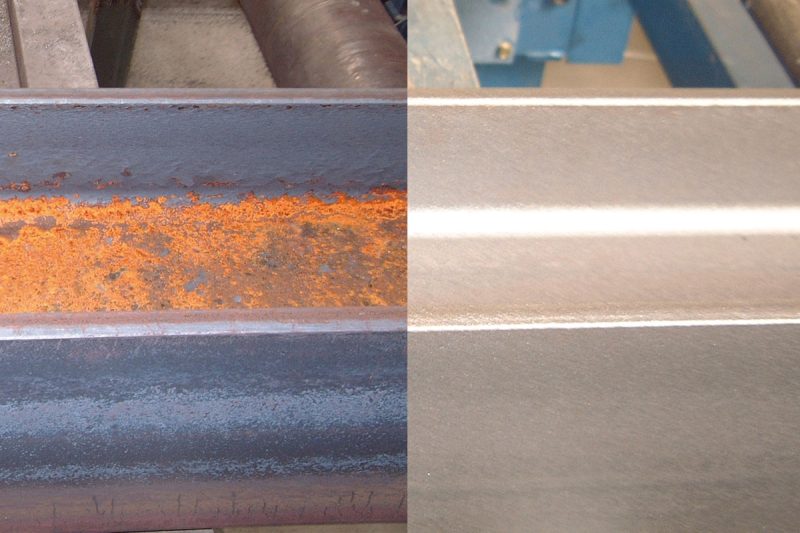

Sandblasting Rust Removal
What is Sandblasting Rust Removal?
How Does It Work?
The Sandblasting Process
- Abrasive Material Selection: The choice of abrasive material, such as silica sand, glass beads, aluminum oxide, or steel grit, depends on the surface material and desired finish.
- Blasting Equipment Setup: The abrasive material is loaded into a blasting machine, which uses compressed air or pressurized liquid to propel the abrasive at high speeds.
- Abrasive Impact: The abrasive particles strike the rusted surface, physically removing the rust layer through a combination of kinetic energy and erosion.
- Surface Cleaning: The abrasive media dislodges the rust, leaving a cleaned surface ready for further treatment, such as painting or coating.
Types of Sandblasting
- Dry Sandblasting: Uses dry abrasives; most common for rust removal.
- Wet Sandblasting: Combines water and abrasive to reduce dust and heat generation.
- Vapor Blasting: A gentler method using water, abrasive, and compressed air for a finer finish.
Abrasive Materials Commonly Used
- Silica Sand: Effective but poses significant health risks.
- Glass Beads: Provides a smooth finish; often used for delicate materials.
- Steel Grit or Shot: Aggressive cleaning for heavy-duty applications.
- Organic Media: Such as walnut shells or corn cob, used for softer materials or less aggressive cleaning.
Advantages of Sandblasting Rust Removal
- Cost-Effective: Sandblasting equipment is generally less expensive than laser systems, making it accessible for small businesses and large-scale operations alike.
- Efficiency for Large Areas: Sandblasting is highly effective for cleaning extensive surface areas quickly, making it suitable for large structures like bridges, ship hulls, and industrial machinery.
- Surface Preparation: The abrasive action creates a textured surface, ideal for enhancing the adhesion of coatings or paints.
- Versatility: Sandblasting can be used on a wide variety of materials, including metal, wood, and concrete, and is effective for removing rust, paint, or dirt.
- Ease of Use: Operators can quickly learn the basics of sandblasting, and the equipment is straightforward to operate with minimal technical expertise.
Disadvantages of Sandblasting Rust Removal
- Risk of Surface Damage: The abrasive impact can erode or deform delicate components or thin metal surfaces, making it unsuitable for precision applications.
- Dust and Waste Generation: Sandblasting produces large amounts of waste material and airborne dust, necessitating additional cleanup and waste disposal.
- Environmental Concerns: The abrasive media and removed rust particles can pollute the surrounding environment if not properly contained.
- Health Hazards: Operators are exposed to potential health risks from dust and abrasive particles, requiring stringent safety measures.
- Inconsistent Results: Achieving uniform cleaning across the surface can be challenging, especially with manual operation.
- Limited Automation Potential: Sandblasting is less suited for automation and may require significant manual labor for large-scale projects.
Environmental and Health Concerns
Environmental Impact
- Dust and Air Pollution: Sandblasting generates substantial airborne dust, which can spread rust particles, abrasive media, and contaminants into the environment.
- Waste Management: Spent abrasive materials and rust debris must be collected and properly disposed of to prevent soil and water contamination.
- Water Usage in Wet Methods: Wet or vapor blasting requires water, which may contribute to wastewater management challenges.
Health Risks to Operators
- Silicosis: Inhalation of crystalline silica dust from traditional sandblasting can lead to silicosis, a severe and potentially fatal lung disease.
- Eye and Skin Irritation: Flying abrasive particles can cause eye injuries and skin abrasions if proper protective gear is not used.
- Hearing Damage: The noise levels from sandblasting equipment are high, necessitating the use of ear protection.
- Respiratory Problems: Operators require respirators to protect against inhalation of fine dust and abrasive particles.
Mitigation Measures
- Protective Gear: Operators must wear respirators, goggles, gloves, and full-body suits to minimize exposure.
- Ventilation Systems: Effective dust extraction and ventilation systems reduce airborne contaminants in the workplace.
- Eco-Friendly Abrasives: Using recyclable or biodegradable media, such as crushed glass or sponge media, can reduce environmental impact.
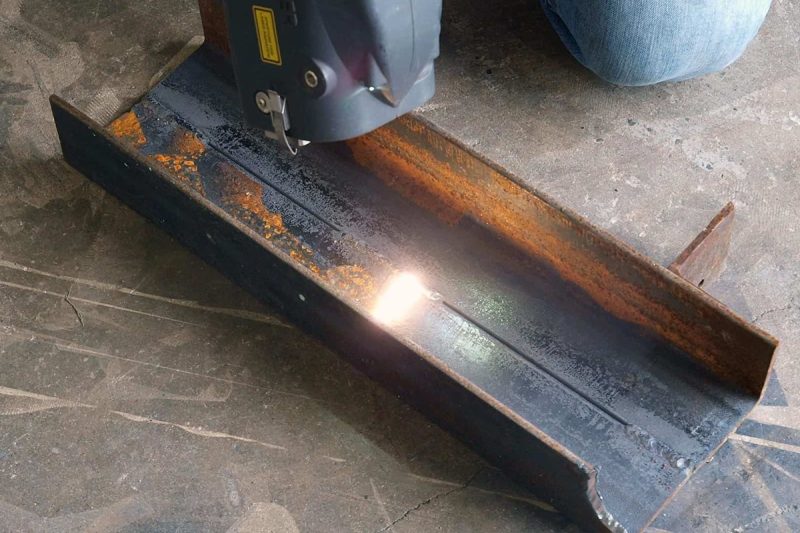

Comparative Analysis
Efficiency and Speed
Laser Rust Removal
Laser rust removal is highly efficient for precision cleaning and applications where detailed work is required. It works effectively on small to medium surfaces, providing consistent results with minimal operator intervention. However, its focused beam and methodical cleaning process mean it can be slower when dealing with large surface areas.
- Efficiency: Ideal for intricate designs and selective rust removal.
- Speed: Slower on large-scale projects compared to sandblasting.
Sandblasting
Sandblasting excels in removing rust over large surface areas quickly, making it the preferred method for extensive cleaning tasks such as ship hulls, bridges, and industrial equipment. However, the manual nature of sandblasting can lead to uneven cleaning in some cases.
- Efficiency: Best suited for large-scale, less precise tasks.
- Speed: High for large-area coverage, but less precise.
Precision and Surface Integrity
Laser Rust Removal
Laser cleaning is known for its high precision. The laser beam can be calibrated to remove rust without damaging the underlying material. It preserves surface integrity, making it ideal for delicate or high-value items like aerospace components or historical artifacts.
- Precision: Excellent, with precise control over rust removal.
- Surface Integrity: Preserves the base material, ideal for sensitive applications.
Sandblasting
Sandblasting is less precise due to its abrasive nature. It can clean surfaces effectively but risks damaging delicate components or altering the material’s texture. This can make it unsuitable for applications requiring a smooth or unaltered surface.
- Precision: Moderate, with a risk of over-cleaning.
- Surface Integrity: May erode or deform thin or fragile materials.
Environmental Impact
Laser Rust Removal
Laser cleaning is an eco-friendly solution with minimal waste. The process generates only rust particles, which can be captured and filtered easily. It eliminates the need for abrasive media or chemicals, making it a sustainable choice.
- Waste Generation: Minimal, primarily rust particles.
- Environmental Footprint: Low, with no hazardous byproducts.
Sandblasting
Sandblasting generates significant waste, including spent abrasive materials and rust debris. The dust created can pollute the air and surrounding environment. Wet sandblasting reduces dust but requires water management, increasing its environmental footprint.
- Waste Generation: High, including abrasive media and dust.
- Environmental Footprint: Significant, especially with traditional abrasives.
Safety Considerations
Laser Rust Removal
Laser rust removal requires specific safety protocols, such as using laser safety goggles and enclosures to protect against accidental exposure. However, it creates a cleaner and safer working environment due to the absence of airborne particles or hazardous chemicals.
- Operator Safety: High, with proper safeguards in place.
- Workplace Hazards: Minimal, as there are no abrasives or dust.
Sandblasting
Sandblasting poses several safety risks, including inhalation of dust, exposure to silica particles, and noise hazards. Operators need extensive protective gear, and work environments require proper ventilation to mitigate risks.
- Operator Safety: Moderate to low without adequate protection.
- Workplace Hazards: High, with risks of silicosis and other health concerns.
Cost Analysis
Laser Rust Removal
The initial investment in laser cleaning equipment is high, but operational costs are low due to minimal consumables and reduced waste management. Over time, it offers cost savings for applications that require consistent precision and efficiency.
- Initial Cost: High.
- Operational Cost: Low, with long-term savings.
- ROI: High for precision and repetitive applications.
Sandblasting
Sandblasting has a lower initial cost, but ongoing expenses for consumables like abrasive media, maintenance, and waste disposal can add up. It is more economical for short-term or large-scale, less precise projects.
- Initial Cost: Low.
- Operational Cost: High, with recurring expenses.
- ROI: Better for short-term, large-scale tasks.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Laser Rust Removal
Laser systems require minimal maintenance, with routine checks on the laser source and cooling systems. The lack of consumables reduces downtime and operational interruptions. Operators may need specialized training to maximize efficiency.
- Maintenance: Low, with few consumables.
- Operational Interruptions: Minimal.
- Training Requirements: Moderate.
Sandblasting
Sandblasting equipment requires frequent maintenance, including replacing abrasive materials, cleaning equipment, and managing waste. It also necessitates regular inspections to ensure safety and performance.
- Maintenance: High, with regular replenishment of media.
- Operational Interruptions: Frequent due to cleaning and media replacement.
- Training Requirements: Basic to moderate.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Laser Rust Removal
Laser systems require minimal maintenance, with routine checks on the laser source and cooling systems. The lack of consumables reduces downtime and operational interruptions. Operators may need specialized training to maximize efficiency.
- Maintenance: Low, with few consumables.
- Operational Interruptions: Minimal.
- Training Requirements: Moderate.
Sandblasting
Sandblasting equipment requires frequent maintenance, including replacing abrasive materials, cleaning equipment, and managing waste. It also necessitates regular inspections to ensure safety and performance.
- Maintenance: High, with regular replenishment of media.
- Operational Interruptions: Frequent due to cleaning and media replacement.
- Training Requirements: Basic to moderate.
The choice between laser rust removal and sandblasting depends on specific project requirements:
- Choose Laser Rust Removal for precision, minimal environmental impact, and long-term cost efficiency in industries like aerospace, electronics, and heritage restoration.
- Choose Sandblasting for fast, cost-effective cleaning of large-scale structures or applications where surface alterations are acceptable.
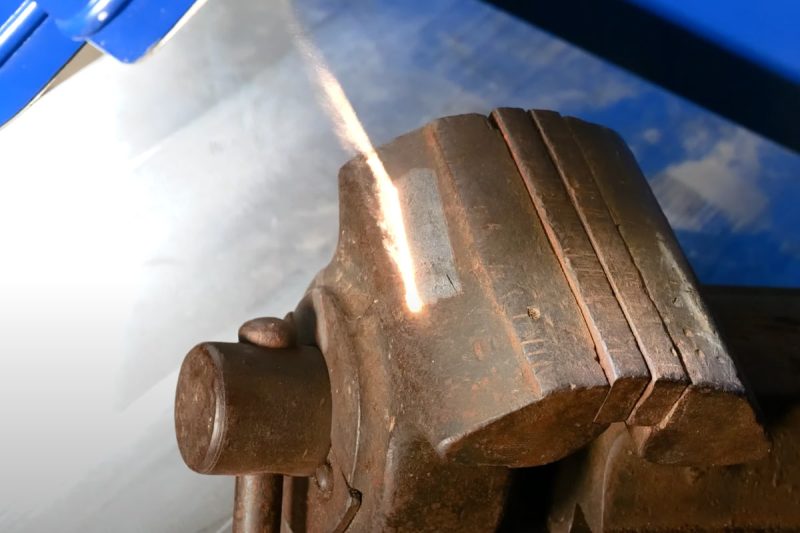

Industry-Specific Applications
Automotive Industry
- Laser Rust Removal: In the automotive industry, precision and surface integrity are critical. Laser rust removal is ideal for restoring classic car parts, cleaning delicate engine components, and removing rust from intricate areas such as weld joints and thin panels. The non-contact nature of laser cleaning ensures that the base metal is preserved, maintaining the structural and aesthetic integrity of high-value components. It is also used for surface preparation before applying protective coatings, ensuring strong adhesion.
- Sandblasting: Sandblasting is often used for large automotive components, such as chassis frames and body panels, where speed is a priority. However, its abrasive nature can pose a risk of over-cleaning or deforming thin metal parts, making it less suitable for detailed work.
Aerospace Industry
- Laser Rust Removal: The aerospace industry demands the highest levels of precision and cleanliness due to the safety-critical nature of its components. Laser rust removal excels in cleaning delicate aircraft components, such as engine blades, fuselage panels, and landing gear, without altering their dimensions or compromising material strength. It is also valuable for removing coatings or contaminants during maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) operations.
- Sandblasting: Sandblasting is used in aerospace applications primarily for surface preparation or cleaning non-precision parts. However, its abrasiveness can lead to surface erosion, which is not acceptable for high-value or critical components.
Heritage and Conservation
- Laser Rust Removal: In heritage and conservation, laser cleaning is a revolutionary technology used to restore historical artifacts, sculptures, and monuments. It allows precise rust and dirt removal without damaging the underlying materials, such as bronze, steel, or even delicate patinas. Laser cleaning is also highly controllable, making it suitable for preserving intricate details and textures on historical items.
- Sandblasting: While sandblasting can clean large stone or metal surfaces, it is generally avoided in conservation due to its abrasive nature, which can erode fine details and cause irreversible damage to delicate or ancient artifacts.
Shipbuilding and Marine Applications
- Laser Rust Removal: Laser cleaning is gaining traction in the marine industry for tasks such as removing rust and marine growth from ship components, propellers, and hull sections. It is especially effective for localized cleaning and preparing surfaces for repairs or coatings. Its eco-friendly nature is a significant advantage in marine environments where contamination and waste must be minimized.
- Sandblasting: Sandblasting has traditionally been the standard method for large-scale cleaning in shipbuilding and marine applications. It is highly effective for removing rust and scale from hull exteriors, decks, and large structural components. However, it generates significant dust and waste, requiring containment measures to prevent environmental pollution.
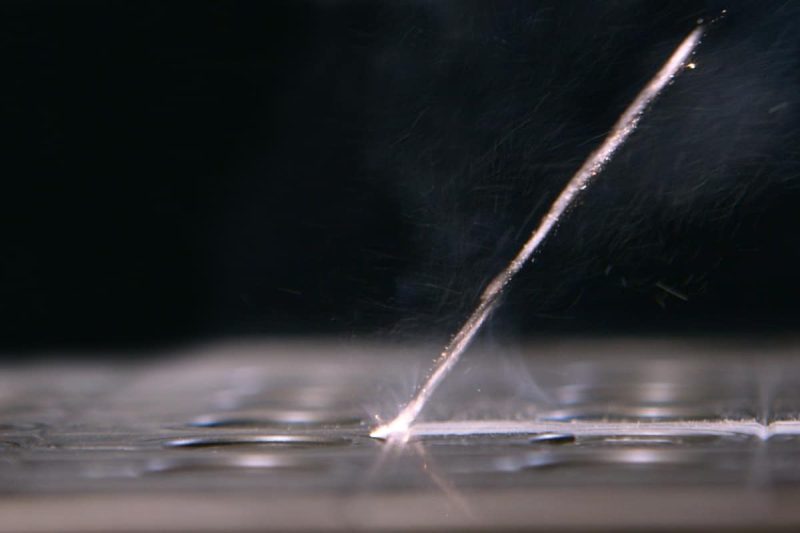
Economic Considerations
Cost Breakdown
Laser Rust Removal
Laser rust removal systems have a high initial investment cost, primarily due to the advanced technology involved. However, the operational expenses are relatively low, as the process does not require consumable materials like abrasive media or chemicals.
- Initial Costs: Laser cleaning machines range from $10,000 to $100,000, depending on the power, portability, and automation features.
- Operational Costs: Minimal, as the process uses only electricity and requires little maintenance. There are no recurring costs for consumables, and waste management is simple due to minimal byproducts.
- Training Costs: Operators may need specialized training to handle laser systems effectively, adding a one-time expense.
Sandblasting
Sandblasting equipment is generally less expensive upfront, making it a cost-effective option for businesses with limited budgets. However, the ongoing costs for consumables, maintenance, and waste management can accumulate over time.
- Initial Costs: Basic sandblasting setups cost between $1,000 and $10,000, with additional costs for compressors and nozzles.
- Operational Costs: High, due to the constant need for abrasive materials, equipment wear and tear, and waste disposal. Abrasive media costs vary depending on the type used, ranging from $10 to $50 per bag.
- Maintenance Costs: Equipment requires regular cleaning and part replacement, increasing the overall expenditure.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Laser Rust Removal
Laser rust removal offers a higher ROI in the long term, especially for industries requiring precision, minimal waste, and eco-friendly operations. The efficiency and durability of laser systems contribute to long-term savings.
- Durability: Laser systems have a long operational life, often exceeding 10 years, with minimal downtime and low maintenance requirements.
- Time Savings: The precision and automation potential of laser cleaning reduce labor costs and increase productivity.
- Sustainability: The eco-friendly nature of laser cleaning aligns with modern environmental regulations, reducing compliance costs.
Sandblasting
Sandblasting can provide a quick ROI for short-term projects or businesses focused on large-scale rust removal tasks. However, the cumulative costs of consumables and waste management reduce its cost-effectiveness over time.
- Quick Returns: Suitable for projects where initial investment needs to be recouped quickly.
- Operational Limitations: Higher recurring costs and potential regulatory challenges due to waste generation can impact long-term profitability.
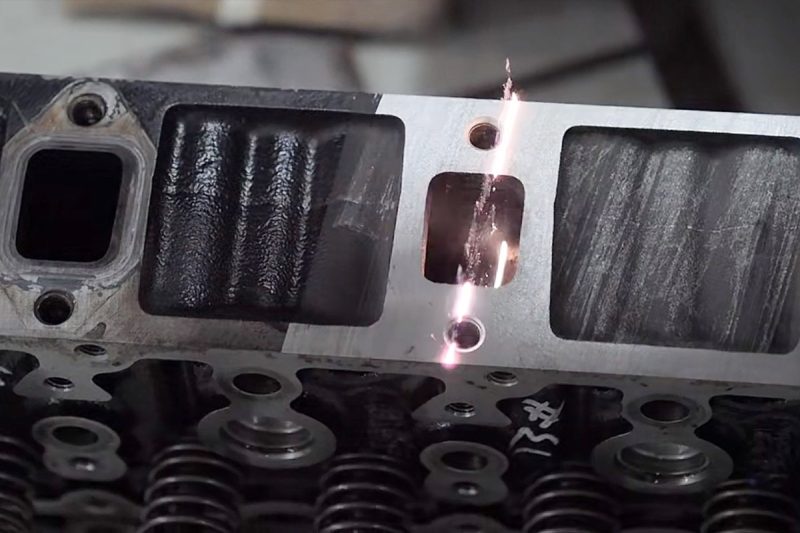

Environmental and Regulatory Compliance
Environmental Regulations
Laser Rust Removal
Laser rust removal is widely recognized as an environmentally friendly solution due to its minimal waste generation and absence of hazardous byproducts. The process vaporizes rust into fine particles, which can be easily captured with filtration systems, making it compliant with stringent environmental laws.
- Minimal Waste: Unlike sandblasting, laser cleaning does not produce large amounts of debris or spent abrasives. This reduces the burden on waste disposal systems and minimizes environmental contamination.
- Chemical-Free: Laser rust removal eliminates the need for abrasive media or harsh chemicals, further reducing the environmental footprint.
- Compliance with Standards: Laser systems align with modern environmental regulations, including those governing air quality and waste management, making it easier for businesses to meet compliance requirements.
- Energy Consumption: While lasers consume electricity, advancements in energy-efficient systems help reduce overall power usage, contributing to sustainability goals.
Sandblasting
Sandblasting, although effective for large-scale rust removal, poses several environmental challenges due to the generation of waste and airborne pollutants.
- Abrasive Waste: Sandblasting produces large volumes of spent abrasive media, rust debris, and dust, which require proper disposal to avoid soil and water contamination.
- Dust and Air Pollution: Dry sandblasting generates significant airborne particles, contributing to air quality issues and necessitating containment measures.
- Water Usage in Wet Methods: Wet and vapor blasting require water, creating additional challenges in wastewater management.
- Regulatory Challenges: Stricter environmental laws surrounding dust emissions and waste disposal can increase operational costs for businesses relying on sandblasting.
Workplace Safety Standards
Laser Rust Removal
Laser rust removal provides a safer work environment, reducing many of the hazards associated with abrasive processes. However, the technology still requires adherence to strict safety protocols.
- Laser Safety Measures: Operators must use protective eyewear and adhere to safety guidelines to prevent exposure to the laser beam. Enclosed or automated systems can further enhance safety.
- Cleaner Work Environment: The process generates minimal dust or debris, reducing the need for respiratory protection and improving overall workplace air quality.
- Noise Levels: Laser cleaning operates relatively quietly compared to sandblasting, minimizing the risk of hearing damage.
- Ease of Compliance: With fewer physical hazards, laser cleaning simplifies compliance with workplace safety regulations.
Sandblasting
Sandblasting is associated with several occupational hazards, requiring extensive safety measures to protect workers.
- Respiratory Risks: Operators are exposed to fine dust and abrasive particles, increasing the risk of respiratory diseases such as silicosis.
- Protective Gear: Workers must wear full-body protective suits, gloves, goggles, and respirators to minimize exposure.
- Noise Pollution: Sandblasting equipment generates high noise levels, necessitating the use of hearing protection.
- Injury Risk: The high-pressure blasting process can cause injuries if equipment malfunctions or safety protocols are not followed.
- Compliance Requirements: Meeting safety standards involves significant investment in protective gear, ventilation systems, and training, adding to operational costs.
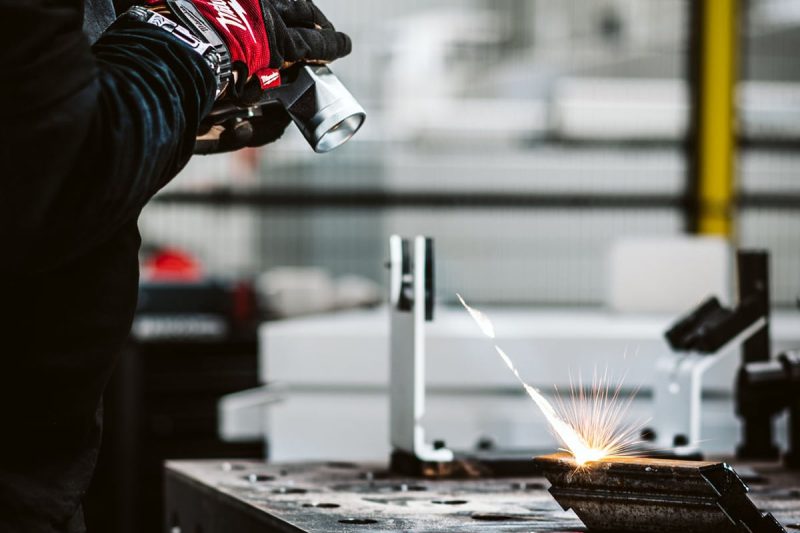

Choosing the Right Rust Removal Method
Key Factors to Consider
- Environmental Impact: If your project prioritizes sustainability and minimal waste generation, laser rust removal is the superior option. It generates almost no hazardous byproducts, aligns easily with modern environmental regulations, and eliminates the need for abrasive media or chemicals.Sandblasting, while effective, produces significant waste and dust, which require containment and proper disposal to meet regulatory requirements.
- Workplace Safety: Laser rust removal offers a cleaner and safer work environment. It reduces airborne particles and noise pollution, minimizing risks to operators. Sandblasting, on the other hand, requires extensive protective measures, including respirators, full-body suits, and ventilation systems, to protect workers from dust and debris.
- Project Size and Precision: For precision tasks involving intricate designs or delicate materials, laser rust removal is the ideal choice. Its ability to target specific areas without damaging the underlying surface makes it suitable for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and heritage conservation. For large-scale projects like shipbuilding or industrial equipment cleaning, sandblasting may be more efficient, especially when precision is less critical.
- Cost and ROI: Laser rust removal involves higher initial costs but offers long-term savings due to minimal maintenance, low operational expenses, and eco-friendly compliance. Sandblasting is more affordable upfront but incurs ongoing costs for consumables, equipment wear, and waste management. Businesses should evaluate their budgets and expected project durations to determine the best ROI.
- Regulatory Compliance: Businesses operating in industries with strict environmental and safety regulations, such as aerospace or marine applications, will benefit from the ease of compliance that laser rust removal provides. Sandblasting may involve additional challenges due to waste disposal and air quality requirements.
When to Choose Laser Rust Removal
- Environmentally conscious operations: Minimal waste and chemical-free process.
- Precision cleaning: Suitable for sensitive components and intricate surfaces.
- Automation potential: This can be integrated into production lines for efficiency.
- High-value industries: Aerospace, automotive, and heritage restoration.
When to Choose Sandblasting
- Large-scale cleaning: Ideal for shipbuilding, industrial equipment, and large structures.
- Short-term projects: Lower initial investment for immediate use.
- Surface preparation: Creates a textured surface for coating or painting.
- Budget constraints: Affordable upfront costs for small businesses.
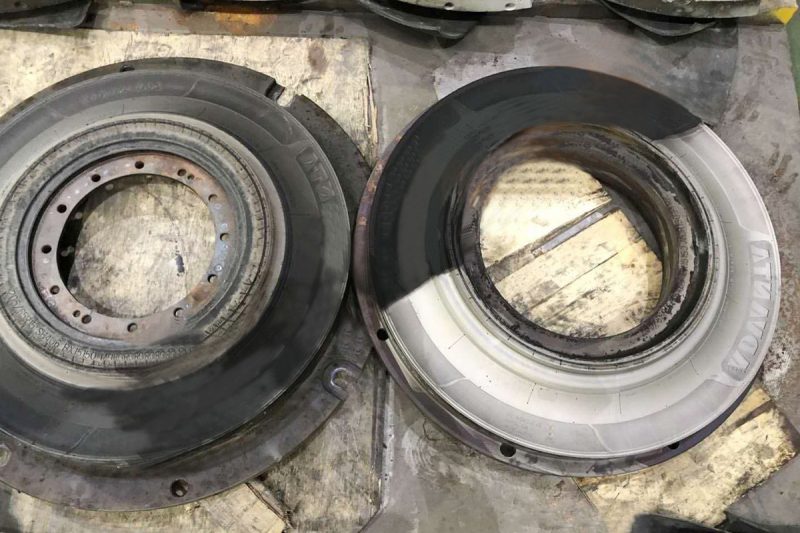

Summary

Get Laser Rust Removal Solutions
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- +86-19963414011
- No. 3 Zone A, Lunzhen Industrial Zone,Yucheng City , Shandong Province.
